We have full services for hearing assessment of all age groups :(1yr to any age). After testing, if needed an ENT appointment may be made. If needed a hearing aid consultation is booked. Our team of audiologists discuss the findings and prescribe the best suitable hearing aids to the patient. We work with all the major manufacturers and our staff is well versed with the latest technology.\


The child (and typically the parent) is seated in a sound booth. Sounds of varying intensity are presented to the child via calibrated speakers or earphones. The sounds may consist of speech or music as well as specific frequencies that are critical to access (hear) the different sounds of speech. The audiologist looks for and records the child’s responses to the softest sounds presented and plots them out on a graph called an audiogram. Behavioral hearing tests include the following methods for the following developmental ages:


Tinnitus is the perception of sound within the human ear in the absence of corresponding external sound. Tinnitus is not a disease, but a symptom that can result from a wide range of underlying causes: like hearing loss associated with exposure to loud sounds or any infections. Up to 17% of normal people can have tinnitus in their ears. Most of the people are not annoyed by it and can live normal life, but in some patients it becomes so severe that it affects the normal day to day routines or functions of the sufferer. In those case a comprehensive test battery is performed and to find out the cause of tinnitus and a strategy is adapted to help the patient cope with tinnitus.

Modern hearing aids are digital and use sound processing strategies to increase or decrease certain frequency of sounds and provide more speech clarity in noisy situations.
However, not every hearing loss is the same and not all hearing aids provide the same type of amplification. The prospective hearing aid user will be informed about the realistic benefit that a hearing aid may provide. A well fitted hearing aid will significantly improve an individual’s ability to communicate in their every day lives.

This is the most simple, reliable method to assess hearing. The patient sits in a sound booth and is presented with a series of tones to determine the level of hearing. This serves as a baseline test for all the hearing and balance testing including hearing aid prescription and fitting.
Tympanometry is the measure of immittance of the eardrum; in other words how easy or how hard it is for sound waves to travel into the inner ear.
Acoustic Reflexes: Not only can your knee jerk but your ears have a reflex too! With high input sounds, the muscles reflex in your middle ear cavity is measured by the stiffness of the eardrum.

This test takes advantage of small acoustical signals that emit from the outer hair cells located in the cochlea of the inner ear.
These signals can be recorded in the ear canal by a sensitive microphone and can give information regarding the cochlear portion of the inner ear. These are measured by non-invasive means of placing a probe in the ear canal and recording the responses to stimulus. This is a very good screening test for infants and non cooperative children

Auditory evoked Brainstem potentials (BAEPs) are very small electrical voltage potentials which are recorded in response to an auditory stimulus from electrodes placed on the scalp. They reflect neuronal activity in the auditory nerve, cochlear nucleus, superior olive and inferior colliculus of the brainstem.This test provides objective information about the auditory nerve and its central connections. The main indication is to rule out the possibility of any retrocochlear pathology in cases of asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus. In children it is sometimes used to determine the threshold of hearing.
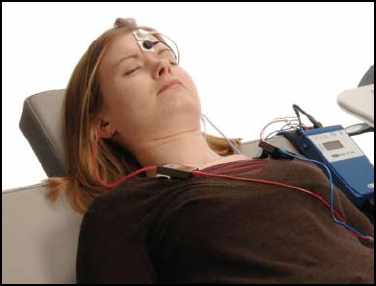
This test provides objective information about the auditory system at the level of the inner ear. This is a simple and non-invasive test for the patient. A soft electrode is placed in the ear canal and a click stimulus is presented through foam earplugs. The test records the inner ear potentials and also can provide information about the auditory nerve and its central connections.
This is one of the diagnostic test for Meniere’s Disease and Endolymphatic hydrops. This is also performed as a Part of dizzy test battery.
