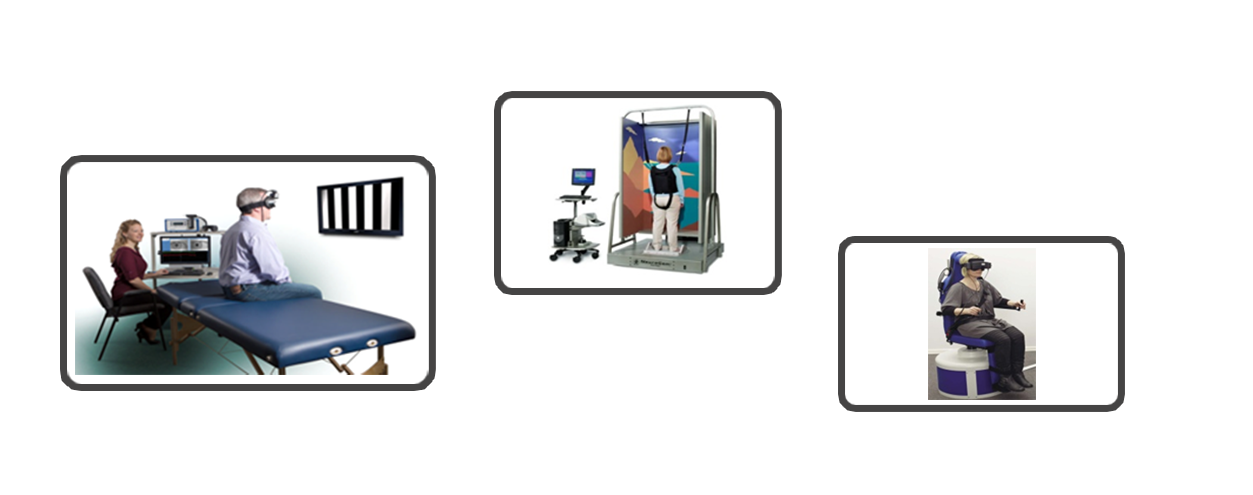
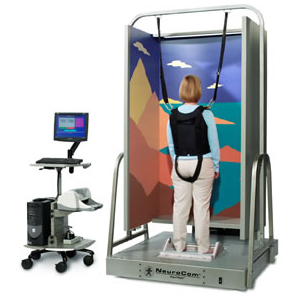
Computerized Dynamic Posturography (CDP) is a unique assessment technique used to objectively quantify and differentiate among the wide variety of possible sensory, motor, and central adaptive impairments to balance control. As such, CDP is complementary to clinical tests designed to localize and categorize pathological mechanisms of balance disorders. CDP can identify and differentiate the functional impairments associated with the pathological processes.
This test evaluates the integration of three main sensory input of human balance system; Inner ear (Vestibule), Eyes, muscles and joints to the brain.
We believe in medical approach to your hearing and Balance disorders. WE have Two Visiting ENT specialists in the clinic. An appointment can be made with the ENT specialists upon referral by your family physician. Our team works in collaboration with each other to provide the best services for hearing and balance disorders.
This is a special clinic. Typically a patient will be referred by the family physician to ENT specialists. After examination the ENT specialist may ask for some special testing to find out the cause of dizziness. Apart from medical treatment by our ENT specialist we also perform repositioning Maneuvers for the treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional vertigo (BPPV).
VRT can be described as systematic repetitive exercises and protocols which extinguish or ameliorate patient’s motion provoked symptoms as well as enhancing postural stability and equilibrium.
But certain vestibular lesions, particularly those that occur with rapid onset, do not benefit from compensation phenomenon. The reasons for failure of compensation:

The Dynamic Visual Acuity Test assesses impairments in a patient’s ability to perceive objects accurately while actively moving the head. In normal individuals, losses in visual acuity are minimized during head movements by the vestibular ocular reflex (VOR) system that maintains the direction of gaze on an external target by driving the eyes in the opposite direction of the head movement. When the VOR system is impaired, visual acuity degrades during head movements. This test can be administered using a traditional Snellen Chart or by new computerized diagnostic methods. The patient is required to move his head side to side and up and down to a computer generated sinusoidal signal. The results are compared with the normative data and analyzed for any abnormality in vestibular system.

Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials: Assesses two important organs in the inner ear that assist with balance; the saccule and the utricle . The vestibulo-collic reflex and the vestibulo-ocular reflex helps pin point the functionality of the vestibular nerve in dizzy patients.
cVEMP Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials:
– Checks for Saccule and Inferior Vestibular nerve (also compliments ABR, tinnitus and retrocochlear pathology).
-The only test which can check the Inferior Vestibular nerve function.
OVEMP Ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials :
-Checks for Utricle and Superior Vestibular nerve (also compliments ABR for retrocochlear pathology)
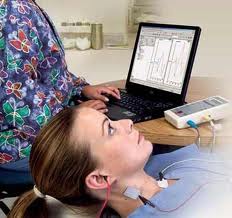
Videonystagmography (VNG) is a technology for testing inner ear and central motor functions, a process known as vestibular assessment. It involves the use of video goggles to trace eye movements during visual stimulation and positional changes. VNG can determine whether dizziness is caused by inner ear disease, particularly Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), as opposed to some other cause such as low blood pressure or anxiety.
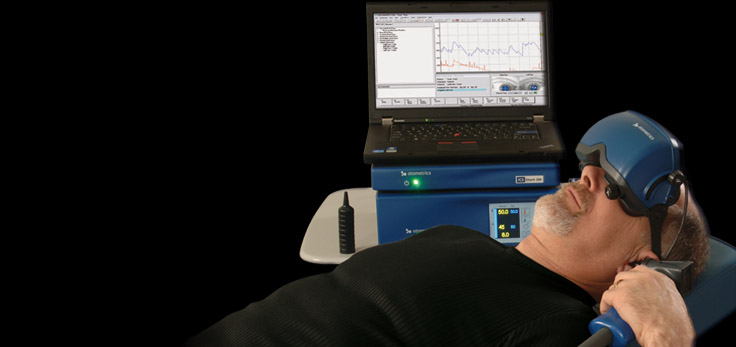
Electronystagmography (ENG) is a diagnostic test to record involuntary movements of the eye caused by a condition known as nystagmus. It can also be used to diagnose the cause of vertigo, dizziness or balance dysfunction by testing the vestibular system.
Technique and Results
The test is performed by attaching electrodes around the eyes or recording eye movements by video camera attached to the goggles and measuring the movements of the eye in relation to the ground electrode. The vestibular system monitors the position and movements of the head to stabilize retinal images. This information is integrated with the visual system and spinal afferents in the brain stem to produce the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). ENG/VNG. It is series of test which include testing for occulomotor function, Positional testing, Optokinetic testing and caloric tests. The caloric test is generally performed by using water (warm and cool) but in cases of perforated eardrums it can be performed by air to irrigate the ears.
The standard ENG test battery consists of:
This is still considered as gold standard test for vestibular testing. While VNG/ENG is the most widely used clinical laboratory test to assess vestibular function, normal ENG test results do not necessarily mean that a patient has normal vestibular function. ENG abnormalities can be useful in the diagnosis and localization of site of lesion; however, many abnormalities are non localizing; therefore, the clinical history and otologic examination of the patient are vital in formulating a diagnosis and treatment plan for a patient presenting with dizziness or vertigo.
The purpose of Rotational Chair Testing is to identify if the vestibular or the neurological system is the cause of a balance disorder. A Rotational Chair Test is performed by securing the patient to a rotary chair which rotates at various speeds and directions while eye movements are being recorded.
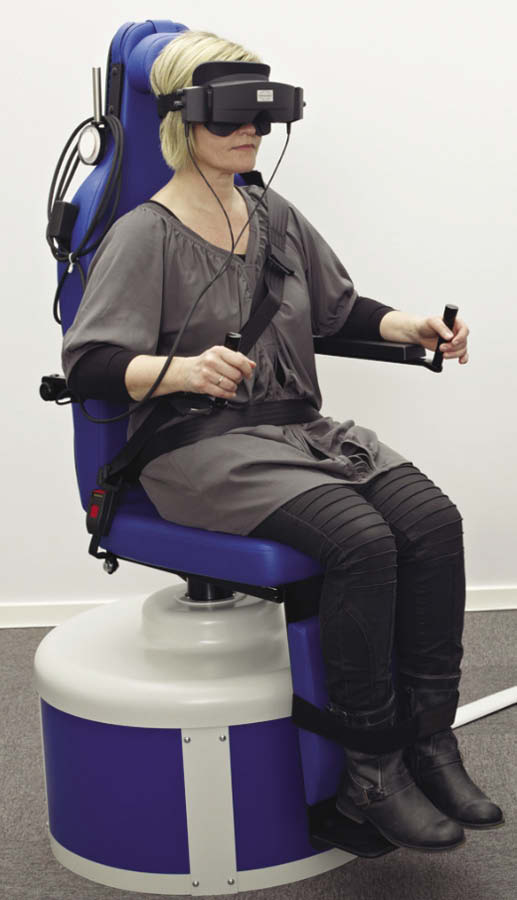
This is the test in which the patient rotates his head back and forth while the body remains stationary. It enables us to expand our ability to evaluate the vestibulo-ocular reflex in its physiological range of function above I HZ. Rotational tests and other ENG test (Caloric) measure the response of the lateral SSC only but with this test we can measure VOR in response to vertical SSC as well. So combined with ENG we are able to provide our patients with a comprehensive diagnostic services.

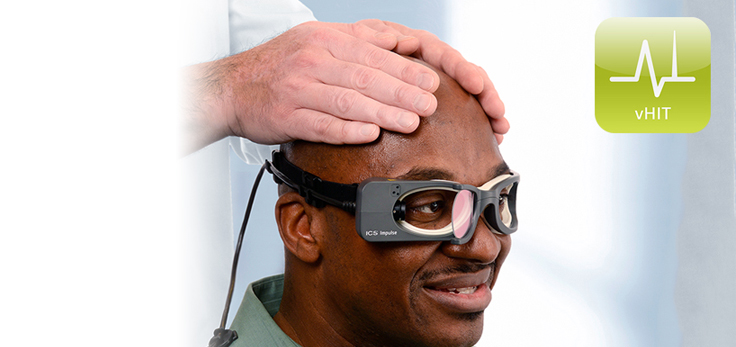
The head impulse test (vHIT) is a test of chronic peripheral vestibular loss. The head thrust test is performed by turning the patient’s head to either side in the angular-horizontal plane to reveal the high-frequency properties of the peripheral vestibular system. This test correlates well with significant excitability reduction indicated via caloric testing.
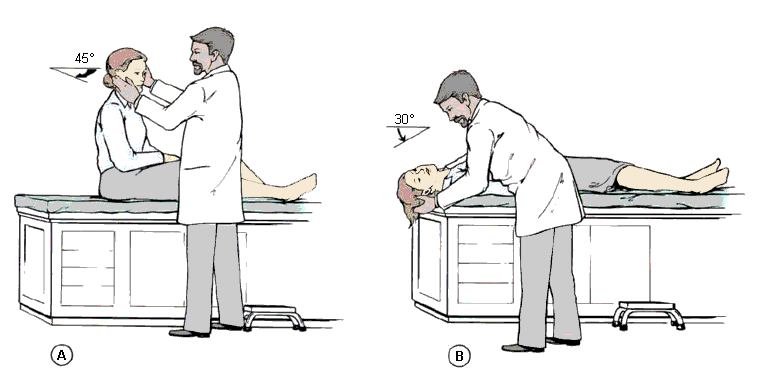
It is described as brief attacks of vertigo and concomitant positioning rotatory linear nystagmus, precipitated by rapid head extension as well as by lateral head tilt towards the affected side. This is the most common cause of vertigo in elderly and is caused by either Cupulolithiasis or Canalilithiasis. These patients with persistent symptoms can be treated most of the time by different repositioning or liberatory maneuvers, depending upon the diagnoses (Canalilithiasis or Cupulolithiasis), canal involved and the ear involved. Once the diagnoses is made it becomes easier for physicians to treat the problem by simple repositioning maneuvers.